🐦UTXOSwap Litepaper: Defining a New Trading Paradigm for Bitcoin Finance
UTXOSwap Overview
UTXOSwap is a decentralized exchange (DEX) protocol for the BTC ecosystem. Its aim is to provide users with a better trading experience and improved execution prices through intent-based trading. Currently, UTXOSwap supports the trading of assets within the RGB++ and CKB ecosystems, with plans to expand support to other BTC ecosystem assets such as Runes.
Currently, the most common forms of DEX are Order book and AMM (Automated Market Maker). Order book DEX is limited by the high cost of on-chain transactions and has not achieved the same level of success as centralized exchanges. On the other hand, AMM has gained wider recognition due to its simple and direct trading concept. However, as on-chain transaction volume and liquidity increase, issues with AMM have also emerged, such as inefficiency, gas fee competition, and the prevalence of MEV (Miner Extractable Value). As a result, intent-based trading models have emerged, combining the advantages of order books and AMM to maximize the experience and benefits for users and liquidity providers. UTXOSwap adopts intent-based trading as its core, utilizing the advantages of UTXO programming to design a new type of DEX.
Thanks to the characteristics of UTXO, UTXOSwap offers many innovations and advantages. In terms of trading mode, UTXOSwap enables off-chain matching and on-chain verification, allowing for the integration of liquidity providers beyond AMM during the matching phase. In terms of performance, the parallelism nature of UTXO significantly improves transaction efficiency. In terms of gas fees, no gas fees are incurred for unmatched intents, and the gas fees for normal transactions are as low as negligible. If certain trading pairs become highly active, a local fee mode can be implemented to isolate their impact on other trading pairs.
UTXOSwap is a crucial infrastructure for the BTC ecosystem, effectively addressing the issues of poor asset liquidity and high transaction costs. It reduces the costs of asset issuance and trading while providing new possibilities. UTXOSwap will explore the unique characteristics of Bitcoin Finance based on the UTXO model, aiming to become the foundational liquidity infrastructure for the Bitcoin ecosystem and promote its prosperity.
Technical Implementation
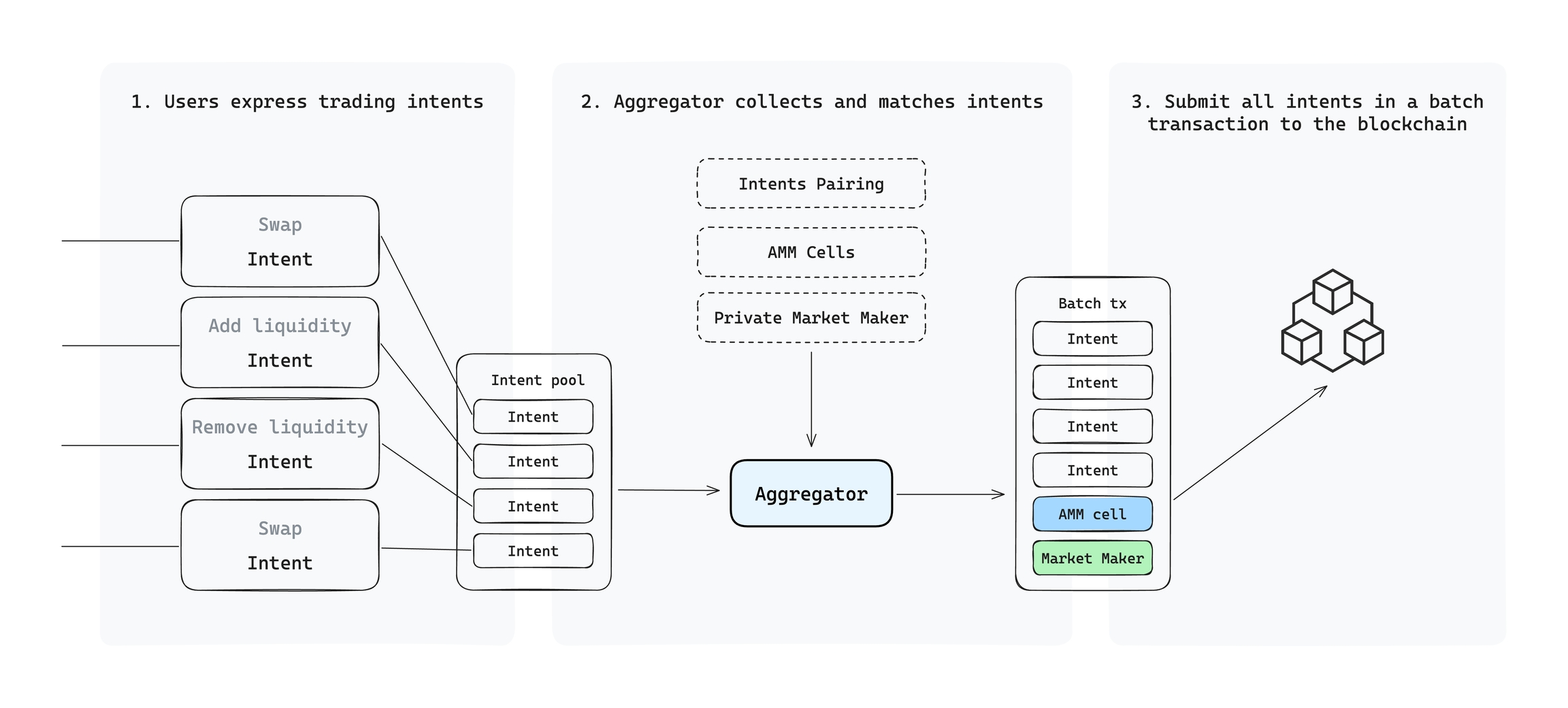
On UTXOSwap, when users engage in swap transactions, it primarily involves the following three steps:
Intent Expression: Users express their transaction intent by signing a message that includes the asset type, amount, and other parameters.
Aggregation and Matching: The aggregator collects all user intents, explores on-chain and off-chain liquidity sources, and performs intent matching.
Transaction Submission: The aggregator assembles all eligible transactions and submits them on-chain.
The liquidity sources that the aggregator can utilize include:
Directly matched user intents
AMM cells (various AMM liquidity pools built on the CKB chain)
Private Market Makers
Intent Cell
The intent cell is used to record the user's transaction intent and ensure that it satisfies specific conditions when consumed. For AMM operations, intents can be divided into three types: Swap, AddLiquidity, and RemoveLiquidity.
When using UTXOSwap, users need to initiate a CKB transaction and record their transaction intent in the intent cell. For example, when a user sets a slippage tolerance and selects a specific liquidity pool for trading, these parameters will be written into the intent cell. When the intent cell is unlocked, the script verifies if the assets returned to the user in the outputs meet the slippage requirements, and checks if the specified liquidity pool cell is included.
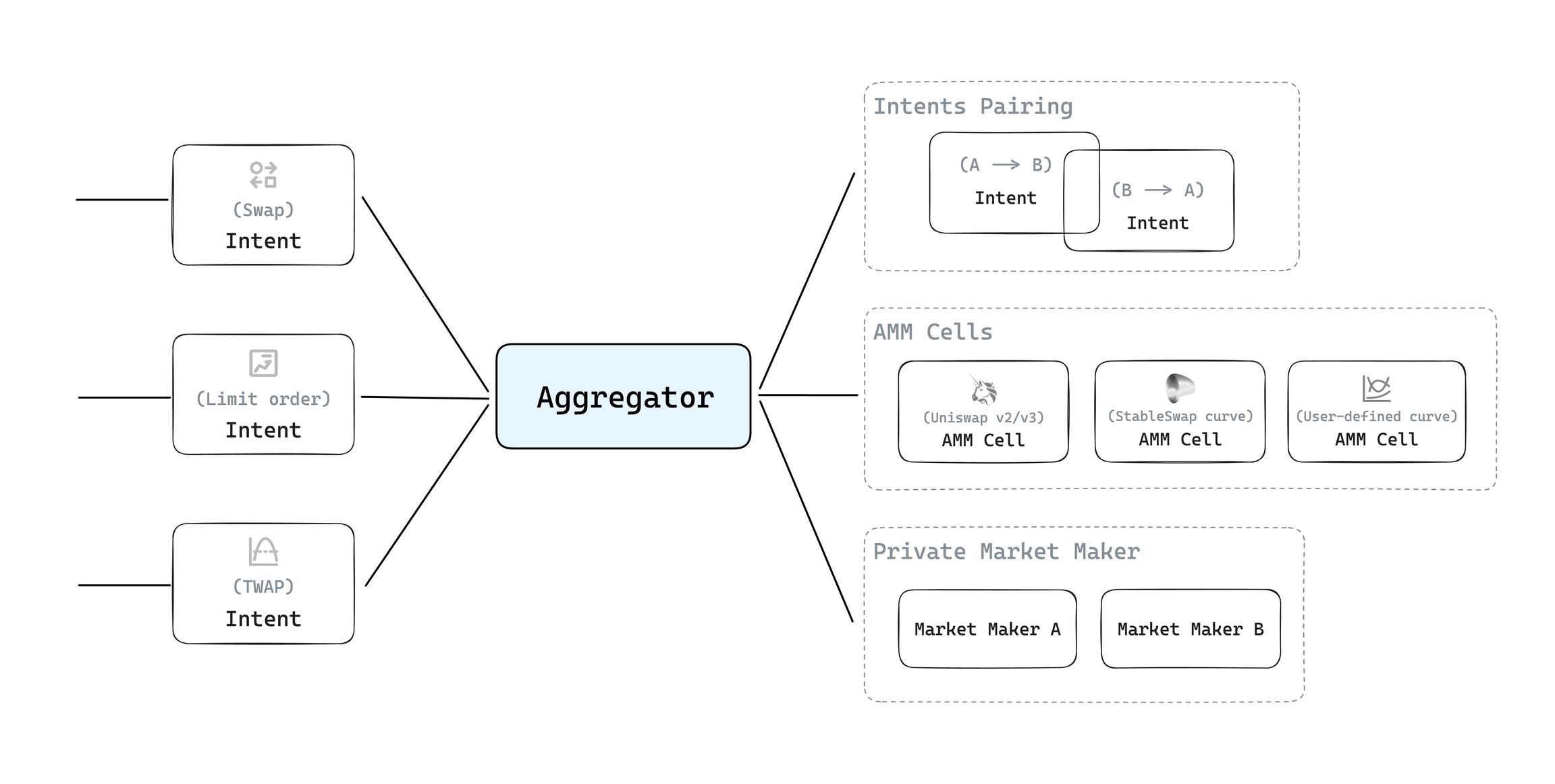
The intent cell supports various forms of transactions. In addition to standard swap transactions, it will also support limit orders and TWAP (Time-Weighted Average Price) transactions. This allows the UTXOSwap platform to cater to complex user trading needs and enhance strategy flexibility. By precisely configuring the parameters in the intent cell, users can have precise control over the conditions and timing of transaction execution, optimizing efficiency and outcomes.
Bitcoin also has a unique feature of supporting PSBT(Partially Signed Bitcoin Transaction ), which allows multiple parties to participate in building the same transaction through partial signatures. In CKB, the corresponding PSBT extension is Open Transaction. With the integration of Open Transaction in UTXOSwap, users can construct transaction intents directly through signing a message off-chain, while others can fulfill these intents by supplementing inputs and outputs, providing a more optimal trading experience.
AMM Cell
The AMM cell is responsible for all the verification logic related to AMM, including verification of intent transactions, management of assets in the liquidity pool, and minting and burning of liquidity tokens.
During the transaction execution process, the AMM cell verifies each transaction intent to ensure user requirements are met. It also checks if the adjustments in the liquidity pool's state strictly follow the defined AMM curve to ensure the overall security of the pool.
Product Advantages
Intent-based Hybrid Trading Model
In traditional AMM models, there are only two participants in each transaction: the user and the liquidity pool. Users can only accept the current quote from the liquidity pool when trading. From the user's perspective, although this model enhances convenience of execution, it limits the possibility of obtaining better execution prices. From the market maker's perspective, passive market-making in creating liquidity pools incurs impermanent loss and loses power of defining prices, while active trading introduces uncertainties such as slippage and MEV.
To address these issues, the intent-based trading model has emerged. In this model, users are no longer passive recipients of prices but actively express their trading intents, such as "exchange 10 A Tokens for at least 20 B Tokens." On liquidity provider side, more ways are developed beyond AMM. If it is profitable, market makers can directly execute trades based on user intents. Even without market maker matching, if the price of the AMM liquidity pool falls within the user's intended range, the transaction can be successfully completed, turning the process into a limit order.
UTXOSwap leverages the characteristics of on-chain verification in the UTXO programming model to achieve off-chain matching and on-chain execution, effectively realizing the intent-based hybrid trading model described above. In the future, we will further expand the user's ability to express intents, such as implementing logic similar to a Dutch auction: the price gradually decreases within a certain range over time, and market makers compete with each other based on their costs until the AMM guarantees the final execution.
Customizable Curves and Fee Rates
In the UTXOSwap AMM model, Liquidity providers can customize the pricing curve based on the characteristics of the assets. For example, trading pairs involving stablecoins can adopt a curve type specific to stablecoins. Additionally, the trading pool offers optional fee rates that allow different liquidity providers (LPs) to have the freedom to choose and maximize their earnings.
Ultra-Low Gas Fees and Pay Gas with Any Token
The gas fee cost for a single transaction in UTXOSwap is approximately 1/10000 of a CKB. Based on the current price of CKB, this amounts to less than 0.000002 (two-millionths) USD, which is negligible. Furthermore, thanks to the off-chain computation nature of UTXO, the feasibility of a user's transaction intent can be verified off-chain. If a transaction cannot be executed, it will not be submitted to the chain, and thus the user does not need to pay any fees.
On the other hand, due to the design of UTXOSwap, users are not required to be aware of the gas fee or the CKB needed for state space. Users can pay these costs seamlessly with any token of their choice. UTXOSwap automatically converts the tokens provided by the user and assists in paying the gas fee or creating new cells.
Compatible with Multi-Chain Wallets, Seamless L1/L2 Operations
Users of UTXOSwap do not need to download and use a specific CKB wallet. Instead, they can directly use their familiar BTC wallet for L1/L2 leaps, L2 transactions, transfers, and other operations. In terms of user experience, a BTC address corresponds to a fixed CKB address, and the control of the CKB address belongs exclusively to the corresponding BTC address. This correspondence is at the chain level, so in other CKB applications compatible with multi-chain wallets, the same BTC address will correspond to the same CKB address.
In addition to BTC, UTXOSwap's technical infrastructure can also support wallets from other major blockchain networks such as ETH, Solana, and Tron. If there are corresponding asset collaboration scenarios in the future, such as cross-chain operations between CKB and Solana, we will also provide support for the respective wallets.
Last updated